📢 Highlights
Genentech’s Concept Bottleneck Model Advances Precision in Protein Design
Novartis and Schrödinger Join Forces in $150M AI- Driven Drug Discovery Deal
Aditum and Leads Biolabs Create Oblenio Bio to Target Autoimmune Therapies
Alphafold3 (finally) Open Sources its Code and Weights for Academic Users
Not yet a member of our super awesome slack community of >8000? Join HERE 🤗
👀 In Case You Missed it ..
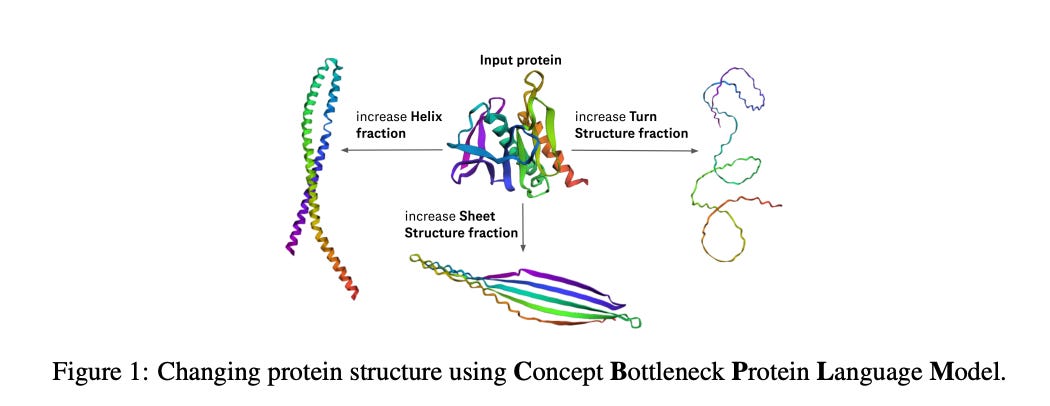
Concept Bottleneck Protein Language Models for protein design
Genentech and Prescient Design researchers introduce Concept Bottleneck Protein Language Models (CB-pLMs), which offer an innovative approach to protein design by integrating a "concept bottleneck" layer, where neurons align with specific biological traits like stability or charge. This enables targeted interventions, improving control over concept values by threefold and enhancing task accuracy by 16% compared to standard models. CB-pLMs perform on par with state-of-the-art models and facilitate debugging through a linear decoder layer, allowing domain experts to assess and address model behaviors without compromising performance, even at a large scale.
Novartis Expands AI-Driven Drug Discovery in $150M Schrödinger Deal
In a unification of industry titans, Novartis has entered into a $150 million collaboration with Schrödinger, allowing Novartis access to Schrödinger's computational drug discovery platform, which employs physics-based machine learning to identify and optimize therapeutic compounds. This collaboration is structured to potentially yield billions in milestone payments if key drug discovery targets are achieved. Schrödinger’s advanced platform leverages extensive molecular modeling and predictive capabilities, which are anticipated to significantly shorten Novartis’s discovery timelines and reduce costs. By integrating Schrödinger’s technology, Novartis strengthens its position at the forefront of AI-accelerated drug discovery, aiming to bring new therapies to market faster.
Behind the Deal: Aditum Bio’s Partnership with Leads Biolabs to Launch Oblenio Bio and Target Autoimmune Diseases
Aditum Bio’s investment in collaboration with China-based Leads Biolabs to establish Oblenio Bio and develop LBL-051, a tri-specific T-cell engager antibody, reflects strategic confidence in the high-growth autoimmune sector. This market segment is projected to reach $153.32 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing prevalence of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Oblenio Bio’s approach, targeting CD19, BCMA, and CD3, is designed to eliminate pathological B-cell populations, offering a more precise and safer alternative to current immunosuppression therapies. Aditum Bio provides the capital and development support, with Leads Biolabs granting exclusive global rights to develop, manufacture, and commercialize the therapy. Leads Biolabs stands to receive up to $35 million in upfront and near-term payments, plus a potential $579 million in milestone payments, royalties on future sales, and an equity stake in Oblenio Bio. Aditum’s prior success, including the $1.9 billion sale of Versanis to Eli Lilly, underscores its track record of nurturing biotech ventures to attract major acquisitions. This partnership aims to accelerate Oblenio Bio’s clinical progress, positioning it as a high-value asset in the autoimmune market and a compelling opportunity for future acquisitions.
Alphafold3 code and weights finally available for academic use
At last, Google Deepmind announced the release of Alphafold3’s code and weights, which will be available for academic use. Six months after the paper's publication and following multiple reproduction efforts by companies like ByteDance or the SF-based startup Chai Discovery, scientists who have an official affiliation to a non-commercial organization (universities, non-profit organizations, and research institutes) can fill out this form to request access.
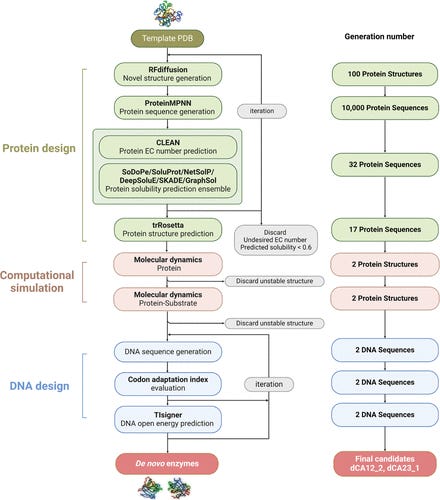
New AI Platform Seeks to Crack Enzymatic Design Code
There's a new entrant in the computational catalysis race - published in ACS Synthetic Biology Journal, GRACE (Generative Redesign in Artificial Computational Enzymology) is an automated workflow for creating de novo enzymes developed by researchers at National Cheng Kung University in Taiwan. The system integrates multiple cutting-edge tools: RFDiffusion for structure generation, ProteinMPNN for sequence interpretation, and CLEAN for enzyme classification, followed by solubility analysis and molecular dynamic simulation. To validate GRACE, the research team successfully identified key motifs in human carbonic anhydrase (hCAII) and created two novel enzymes with demonstrated catalytic activity. GRACE shows promising applications in industrial biocatalysis, where it could enhance chemical process efficiency, as well as in therapeutic applications such as enzyme development and advanced drug delivery systems. The scripts for the workflow are available on GitHub.
Formation Bio, Sanofi, and OpenAI Debut AI-Driven “MUSE”
An innovative AI-based platform designed to accelerate patient recruitment in clinical trials, Muse, has been launched by Formation Bio in collaboration with Sanofi and OpenAI. The platform functions by analyzing data from various sources like electronic health records and social media. MUSE aims to improve recruitment efficiency by reducing average patient matching times and improving cohort diversity. With accurate AI-driven insights, the tool is projected to speed up clinical trial enrollment by up to 50%, potentially decreasing trial durations by several months. MUSE reflects a growing trend of using AI to address long-standing challenges in the drug development process.
Genomic Data Processing with Cloud-Based Workflow Manager wit Closha 2.0
Designed for modern cluster-based infrastructure, Closha 2.0 is a cloud-computing service designed for large-scale genomic data analysis, one of the most computational intensive component of routine sequencing workflows. At its core, the service employs a workflow manager for container orchestration, enabling efficient processing of complex genomic datasets. The platform features an integrated workbench that supports multiple programming languages including Python, R, and shell scripts, while also offering a workbench for data upload, workflow design, and results analysis. Users can also access curated pipelines for standardized analyses. Notably, Closha 2.0 can be useful for the analysis of large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) data. Learn more on the project’s website and dive into the source code on the project’s GitHub.
Atlantis to DevelopNext-Gen Antibody-Drug Conjugates with $181M
With $181 million raised from marqee investors including Novo Holdings, OrbiMed, and Jeito, Swiss biotech Alentis Therapeutics, specializing in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), will advance its next-generation cancer therapeutics. ADCs offer targeted delivery of cytotoxic agents to tumor cells, sparing healthy tissues and reducing side effects. This funding enables the company to refine ADC stability and binding affinity on its two lead programs, which they hope will address long-standing challenges in ADC efficacy and safety. As ADCs gain traction in oncology, this large investment positions the biotech to potentially launch an entire fleet of novel ADCs into clinical trials, meeting the demand for more precise cancer treatments.
Trace Pharma Secures $101M to Advance ALS Treatment Development
San Francisco based Trace Pharma, backed by Third Rock Ventures, has raised $101 million in Series A funding to pursue therapies for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), focusing on targets previously identified in Eli Lilly’s ALS research. The biotech company will use the funding to accelerate preclinical and early clinical studies, especially in exploring therapeutic mechanisms that show promise in slowing ALS progression. With ALS still lacking curative treatments, Trace aims to make strides in targeting disease-modifying pathways, and is seeking to take point position in one of the most challenging indications around.
Workforce Reduction at 23andMe Signals Strategic Realignment
Facing increased financial pressure, 23andMe announced a 40% workforce reduction, impacting approximately 200 employees and a cessation of all drug development programs, as part of a restructuring strategy amid declining stock performance. Once a leader in consumer genetic testing, 23andMe has struggled to expand its health-related services and maintain its position in a competitive market. The company recently faced challenges in securing a buyout offer by CEO Anne Wojcicki, which the board rejected, adding to the instability. This layoff is intended to streamline operations and refocus resources on core genetic and health initiatives to regain stability after a failed take-private bif from its CEO and the subsequent resignation of the companies board.
🗓️ Upcoming BiB Events
See our handy dandy Lu.ma event calendar HERE, please RSVP so folks can plan accordingly!
SF Meets London Biotech, AI, & VC Connect – Friday, November 15th @ London, UK (see invite for location)
Thank you to Vincent Alessi and Robbie Matthews for organizing!
San Francisco AI x Bio: Perspective from those building on the front lines – Wednesday, November 20th
Thank you Lisa Kleinsorge, Shantenu Agarwal, and Ben Kromnick for organizing!
📰 Top Community Conversations
@Craig Shertan asks … are there biotech hubs outside of SF and Boston/Cambridge?
🏢 New Job Openings
Notable postings below - over 100 more on our community job board!
International PhD Programme at MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
Postdoctoral Scientist at MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
Senior Product Manager at Labviva
🙋 🙏 Community Asks
Feedback: How is the Newsletter doing? We’re trying different formats/content. In case the hyperlink above didn’t get your attention, maybe a bright orange button will!
Volunteer: Want to get involved with Bits in Bio, meet new members across the community, and learn about the ecosystem? We are looking for volunteers to help us create great content and manage the community.
🙏 Thank you for being a BiB Weekly reader!
We want to deliver what matters most in Bio AI and would love your feedback on how we can do better. Please weigh in as anon here or DM me directly!