📢 Highlights
ETH Zurich's DeepEST Model Elevates Bacterial Protein Function Prediction
Kivu Bioscience Secures $92M to Advance Safer, More Effective ADCs
AI-Powered C. Diff Treatment from Recursion Moves Forward to Phase 2 Trials
Not yet a member of our super awesome slack community of >8000? Join HERE 🤗
👀 In Case You Missed it ..
Bacterial Protein Function Prediction via Multimodal Deep Learning
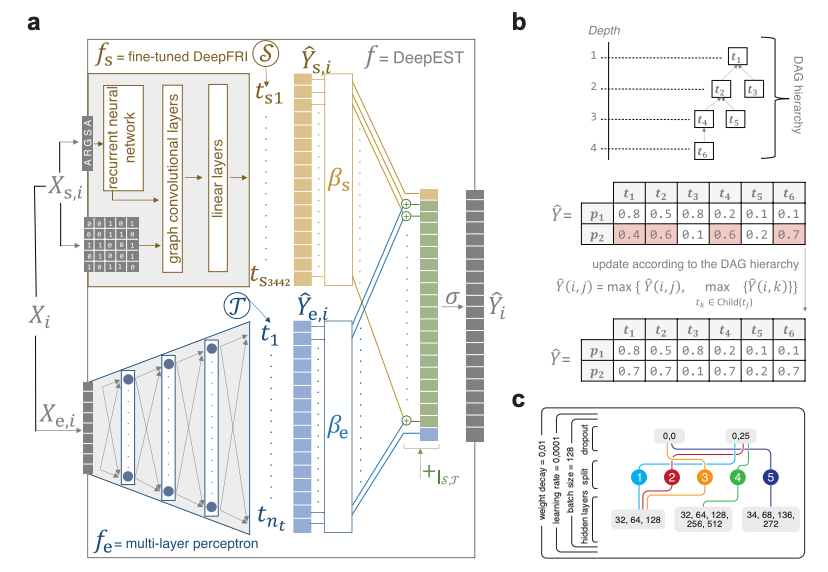
Researchers from ETH Zurich, the Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics and Umea University introduce DeepEST, a multimodal deep learning framework designed to predict bacterial protein functions. This model integrates protein structure, in combination with gene expression, and genomic location data, improving accuracy over traditional methods. DeepEST combines a structure-based model with a multi-layer perceptron that leverages expression data from stress conditions, producing detailed Gene Ontology annotations, particularly for uncharacterized proteins. Applied across 25 bacterial pathogens, DeepEST outperforms sequence-only methods including DeepFRI and DIAMOND, achieving high performance in handling the complex functional redundancy typical of bacterial genomes. Evaluations indicate that DeepEST does a good job handling species-specific models due to its structure-based data partitioning, reducing data leakage when similar protein structures span multiple datasets.This framework shows potential for future expansion, including incorporating additional contextual data, which could improve the precision of protein function annotations, especially for clinically relevant pathogens.To support reproducibility and further development, DeepEST's code is publicly accessible on GitHub.
Behind the Deal: Kivu Bioscience’s $92M Series A to Propel Next-Gen ADCs
Kivu Bioscience’s $92 million Series A, led by Novo Holdings signals confidence in the biotech’s next-generation antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). This investment comes as major players, such as Pfizer (acquiring Seagen) and AbbVie (purchasing ImmunoGen), prioritize ADCs, which offer highly targeted cancer therapies. Kivu’s technology addresses off-target toxicity through enhancing ADC stability - a significant historical limitation in ADCs. Kivu's modifications enable safer, higher dosing and expands the therapeutic window, enhancing efficacy without increasing toxicity or side effects. This stability is critical from an investor standpoint as it broadens patient access, lowers discontinuation rates, and supports sustainable revenue streams. The promising preclinical results indicate potential for treating cancers where conventional ADCs have struggled. This Series A funding accelerates Kivu’s assets toward Phase 1 trials in 2025 and de-risks the pipeline by reducing clinical and regulatory hurdles, positioning them to capitalize on the high-growth ADC market and attract further capital market interest in the coming years.
Recursion's Treatment for C. Diff Enters Phase 2 Trial
Salt Lake Cities flagship biotech, Recursion, has begun Phase 2 trials for REC-3964, an AI-designed treatment targeting recurrent C. difficile infections. Unlike traditional antibiotics, REC-3964 is a small molecule that selectively spares healthy gut microbiota, aiming to reduce the risk of reinfection. Early data suggests a significant reduction in recurrence rates, marking a potential shift in how bacterial infections are managed. The trial will evaluate safety and efficacy in a larger patient cohort over the coming year.
MethylGPT: a foundation model for the DNA methylome
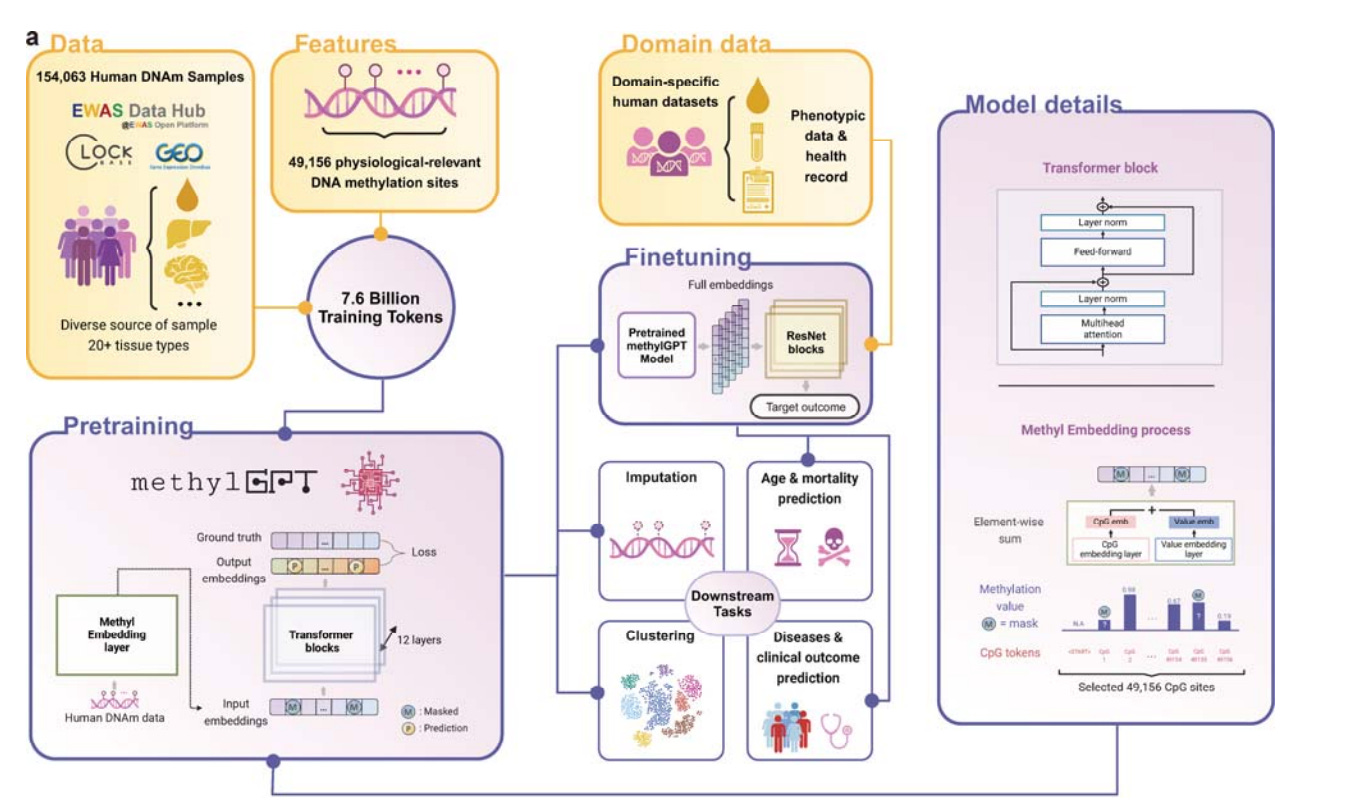
In this new preprint, researchers introduce MethylGPT, a transformer-based model for DNA methylation analysis. The model offers a robust context sensitivity for complex methylation pattern predictions across a variety of datasets. Trained on over 150,000 human samples from 20 tissue types, it captures CpG site patterns with a Pearson correlation above 0.9. It maintains strong performance even with 70% missing data, surpassing traditional models in handling incomplete data sets common in clinical settings. MethylGPT also accurately predicts age and disease risk, identifies age-specific CpG sites, and supports intervention effect analysis, positioning it as a valuable tool in precision medicine. Its embedding and attention mechanisms retain biological context, promoting interpretability and advancing epigenetic research.
Small Molecule Drug Discovery Model Performance: Data Scaling, Multitasking, and Generalization
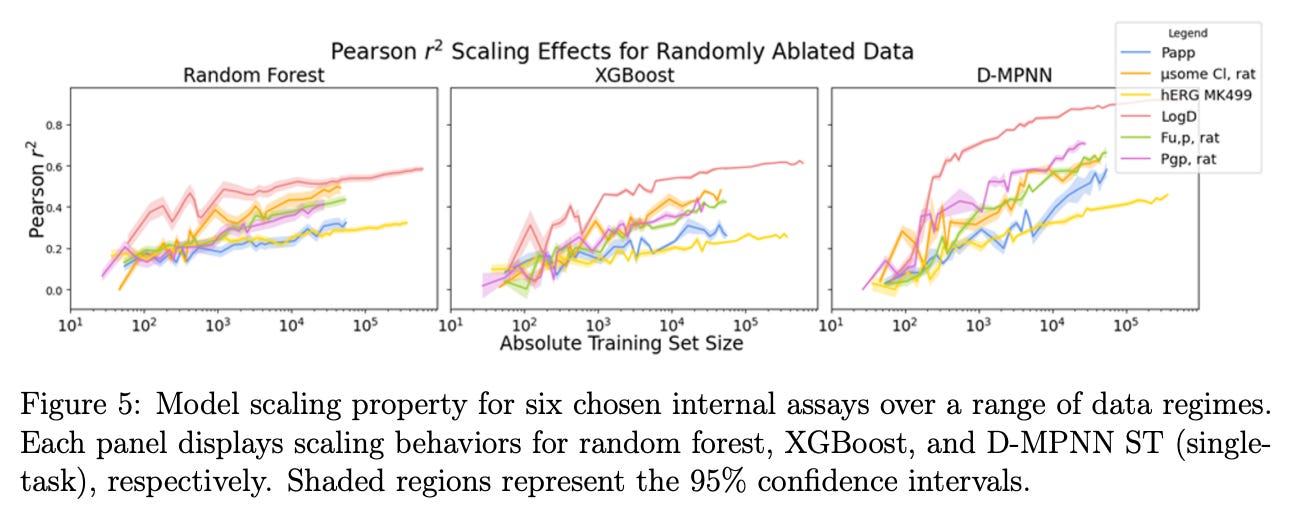
Another preprint, this time by Merck & co proposes a study which examines the impact of data scaling, multitasking, and generalization on predictive models in small molecule drug discovery, particularly for improving ADMET predictions. It finds that directed message-passing neural networks (D-MPNNs) outperform traditional models like random forests and XGBoost, especially with larger datasets and in new chemical spaces. D-MPNNs demonstrate better generalization across unseen chemical properties, while multitask models enhance performance on smaller datasets by minimizing the need for multiple models. Through temporal and random data ablations, they also show that model performance is affected not just by dataset size but also by the similarity between training and testing data, along with the inherent uncertainty of the assays. The research establishes a scaling relationship that explains 81% of the variance in model performance, guiding effective data utilization strategies in drug discovery pipelines.
Advanced Antibody Engineering with AI from the Baker Lab
Archon Biosciences, leveraging cutting-edge AI from David Baker’s lab, has developed Antibody Cage technology to enhance therapeutic precision. This platform uses computational models to engineer cage-like protein structures that can be tailored to fit around antibodies, improving their targeting specificity for hard-to-treat conditions. Initial studies show promising results, with potential applications in oncology and autoimmune diseases. The technology is poised to redefine how biologics are engineered, offering a new layer of control over antibody-drug interactions.
Google Cloud Powers Digital Clinical Trials
Digital clinical trial service provider Medable has expanded its Digital and Decentralized Clinical Trial Platform by integrating it into Google Cloud Marketplace. This collaboration enables AI-powered trial management, data analysis, and patient recruitment, enhancing efficiency and compliance. By leveraging Google’s cloud infrastructure, Medable ensures real-time data sharing and advanced analytics, which can cut trial times significantly. The integration allows for global scalability while maintaining stringent data security measures.
Denmark’s AI Supercomputer Boosts Drug Discovery
Looking to not lose path with international investment, the Novo Nordisk Foundation has invested $87 million to launch Gefion, Denmark’s first AI supercomputer aimed at accelerating research in drug discovery and climate science. With over 250 petaflops of computing power, Gefion can perform complex simulations that were previously infeasible. This infrastructure supports AI-driven models in pharmacogenomics and quantum computing applications, enhancing Denmark’s global research competitiveness. The supercomputer’s capabilities will also aid in developing climate models to better predict environmental changes.
AI Meets High-Fidelity DNA Synthesis in Antibody Development
Bio AI darling, Absci, and Twist Bioscience are collaborating to streamline antibody discovery by merging their AI models with Twist’s DNA synthesis technology. This partnership accelerates the design and validation of antibodies, focusing on high-affinity interactions for immunotherapy applications. Their combined approach promises to reduce development cycles by several months, allowing faster progression from in silico design to in vitro testing. The project aims to address unmet needs in cancer and infectious diseases.
Generative AI Foundation Model for Molecule Discovery
Israeli-based Evogene has teamed up with Google Cloud to create a generative AI foundation model aimed at small molecule discovery for pharmaceuticals and agriculture. Utilizing Google’s Vertex AI and Compute Engine, the collaboration focuses on accelerating the design of bioactive compounds. This partnership will leverage large-scale datasets and machine learning algorithms to optimize the identification of high-potency molecules, potentially revolutionizing drug and crop protection development.
AI-Native Cancer Diagnostic Revolution
Ataraxis AI has launched what they claim to be the world’s first AI-native diagnostic platform, Ataraxis Breast, designed to significantly enhance breast cancer risk assessment. Using deep neural networks trained on millions of imaging data points, the platform delivers up to 30% higher accuracy compared to conventional risk assessments. This increase in precision aims to reduce unnecessary chemotherapy treatments by improving diagnostic specificity. The technology integrates machine learning with radiomics, providing a robust tool for personalized cancer care.
Novel Approaches to Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis from the Column Group
Backed by The Column Group, a new biotech initiative is partnering with Surrozen to explore TGF-Beta-targeting treatments for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The collaboration aims to develop regenerative therapies that address the underlying fibrotic processes in IPF. By harnessing insights into cellular signaling pathways, the project seeks to provide novel therapeutic options for a disease that currently has limited effective treatments. The research could pave the way for more targeted approaches in fibrotic disease management.
Next-Gen Human Biology Database Collaboration
Sapient has entered a partnership with Rancho Biosciences to accelerate the development of a comprehensive human biology database. This resource will integrate multi-omics data to support groundbreaking research in disease mechanisms and drug discovery. The project aims to streamline data analysis and improve the reproducibility of scientific studies. With cutting-edge data architecture, the collaboration will offer researchers unprecedented access to high-quality, integrated biological data.
AI Drug Development with Accenture
The venture arm of the consulting mega-corporation, Accenture, has made a strategic investment in 1910 Genetics to deploy their AI. The collaboration will merge Accenture’s allegedly significant “AI capabilities” with 1910’s multimodal discovery platform, focusing on the rapid design of small molecules and biologics. The integration aims to cut R&D timelines by up to 50%, making treatments more accessible and affordable. This partnership highlights a shift towards more efficient, data-driven pharmaceutical research and consulting organizations looking to achieve 9 and 10 figure integration contracts.
🗓️ Upcoming BiB Events
See our handy dandy Lu.ma event calendar HERE, please RSVP so folks can plan accordingly!
Lausanne Meetup – Tuesday, November 5th @ Debiopharm
Thank you to Thomas Vetterli, Nicolas Stalder, Vincent Lepreux, and Xavier Mesnier for organizing!
Copenhagen Biotech Breakfast – Thursday, November 7th @ Rug Bakery
Thank you to Alexander Junge, Ishani Ummat, Michael Richards, and Sara Sajaniemi-Afonso for organizing, and Benchling for sponsoring!
Houston Meetup – Thursday, November 7th @ Valhalla
Thank you to the organizers Devanshi Pratiher, Janmajay Singh, and Marco Reis!
Washington DC/Maryland/Virginia Happy Hour – Thursday, November 7th @ Northside Social Coffee and Wine
Thanks to Jason Fan for organizing!
📰 Top Community Conversations
It has been a quite the last few days - check back next week for more exciting updates from the BiB Slack!
🏢 New Job Openings
Notable postings below - over 100 more on our community job board!
Staff Data Scientist at Invert
Various Roles at Ataraxis
🙋 🙏 Community Asks
Feedback: How is the Newsletter doing? We’re trying different formats/content. In case the hyperlink above didn’t get your attention, maybe a bright orange button will!
Volunteer: Want to get involved with Bits in Bio, meet new members across the community, and learn about the ecosystem? We are looking for volunteers to help us create great content and manage the community.
🙏 Thank you for being a BiB Weekly reader!
We want to deliver what matters most in Bio AI and would love your feedback on how we can do better. Please weigh in as anon here or DM me directly!